The Return of Collateralised Money
Martin Bartels
8 August 2021
The lifeblood of the modern world, money, remains a divisive subject and often evokes strong emotions. This is mainly because a good part of the effort in the course of a human life goes into acquiring and maintaining money. Terms such as "inflation" or "high taxes" frequently arouse fear, shame and perhaps even aggressive thoughts.
Impassioned debates about the true value of money are as old as money itself, going back perhaps 5,000 years.
Strong feelings are understandable, but they would be an obstacle to rational decisions when means of payment of a new stage of development are at the door. Nothing we need less than fuzzy emotions.
it would be in the interest of society to focus entirely on functionality and then decide how best to deal with the new possibilities.
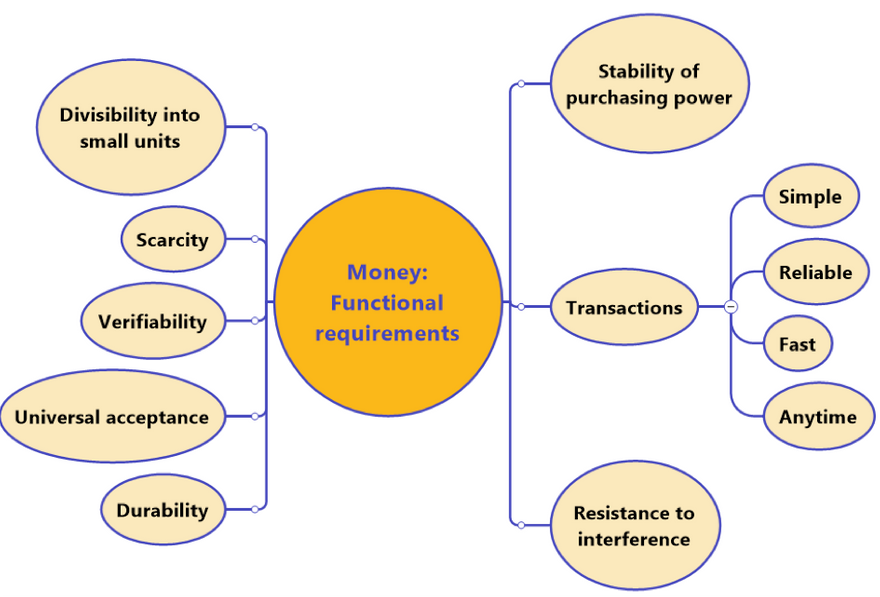
What are the prerequisites for money to be functional?
The requirements for money hardly offer any starting points for controversial discussions:
Chart 1: Money: Functional requirements
Regardless of the physical or electronic manifestation, money is, first and foremost, about functioning in almost all aspects of life. The aforementioned criterion can overlap with other terms . It is important, however, to have a reference system to facilitate the assessment of imminent innovations.
The chart intentionally does not refer to the emotionally charged term "value". It is sufficient to rely on “purchasing power”, which users can acquire, store and transfer.
Money is tied to institutions
Money presupposes an institutional framework. Typically, this is a nation state (or several states together) that
• defines what means of payment are permissible,
• who (central banks and commercial banks) is entitled to issue, what kind, and which volume of money (physical or scriptural),
• sets rules for the operations of the money-issuing institutions,
• monitors the money-issuing institutions’ compliance with the rules and
• empowers a central institution to defend the stability of money in accordance with legal requirements.
The new cryptocurrencies that have emerged in recent years are neither issued by a state nor centralised. Their creation and transfer is not governed by rules that national states have stipulated, yet their rules fulfil the criteria of institutional frameworks. State courts can take corrective action in the case of the usual "accidents" in payment transactions (e.g. theft). States also levy taxes on profits generated by trading in cryptocurrencies.
There are libertarians who have a deep aversion to the institutional foundations of means of payment.
So far, no clear counter-model is discernible that would be suitable for a constructive debate about the pros and cons of a functional alternative. It is therefore still appropriate to accept the key role of legal frameworks and central banks.
Central banks follow their mandate to steer the stability of the currencies they issue. They acquire or dispose of certain assets (e.g. precious metals, deposits in other currencies, securities), they steer the money supply/key interest rates and they manage trust.
The sophisticated methodology available today to stabilise purchasing power of legal tender is the result of institutional learning curves during the 20th century, the course of which often had unintended dramatic implications. For example, the belief in the necessity to collateralise money with gold hindered economic growth as the expansion of the money supply became dependent on the production of mining companies. In crisis situations, central banks were compelled to sell their gold holdings. Afterwards, they found it difficult to provide capital to the productive sector of the economy to recover purchasing power for replenishing their gold stocks.
The final demise not only of the gold standard but of any kind of fixed link between the value of currency units and assets came with the "Nixon shock" on 15 August 1971.
End of the Bretton Woods system
Even in the hearts of some experts, the longing for a "brave old world with a gold standard" may occasionally flare up. The practical implications of such a project, however, are not the subject of this article. Nostalgia is an emotion, not a strategy.
The most impressive achievement is the art of central banks, developed through experimentation in the 20th century, to manage the trust of users of payment instruments. Trust is only an emotion, but the central bankers’ words, gestures and subtle changes of parameters can steer markets today such as the Oracle of Delphi or the Roman augurs did in the past. The efficacy of central bankers’ trust management is beyond doubt.
The development of this sophisticated art that initially rose from the upheavals of the World War I and the slow death struggle of the gold standard was described in detail and in a breath-taking manner by Liaquat Ahamed in his book "Lords of Finance: 1929, The Great Depression, and the Bankers who Broke the World".
The culmination of the art of trust management may have been the US Federal Reserve's successful effort to restore trust after the financial market crisis of 2007 and 2008. The meltdown did not occur.
Malaise
Today there is no small propensity towards monetary malaise. Fears over the stability of assets prices rise when the money supply is allowed to expand, seemingly without limits, and without a plausible connection to the real economy.
The words "helicopter money", "printing press" and the euphemism "quantitative easing" awaken doubts and fears.
Even greater may be the fear of the unknown that may loom if one speaks out against the modern management of trust. There seem to be no alternatives.
At this point it should be emphasised that the concern here is only a growing and hardly explicit uneasiness, because these can be the drivers of new developments. We are not asking whether or not the instruments of central banks are actually reaching their limits.
Clearly there is a growing willingness to consider options that can protect purchasing power from the feared ‘next tempest’.
Technology generates new options
The development of cryptocurrencies that are not dependent on central banks was a first reaction after the financial crisis of 2007/2008. Limiting the number of electronic "coins" issued over the years was and is seen by many as a protection against too much expansion of the money supply, i.e. against inflation.
The arguments are quite similar to those for the protective qualities of precious metals.
Some central banks are working on the introduction of Central Bank Digital Money (“CBDC”) which allows transactions between market participants very quickly and without counterparty default risk. Even after technical perfection is achieved, this will be a subset of normal money that is not collateralised.
There are possibilities to hold a precious metal account with a trustee. There are savings plans and pension plans for this. Balances can be transferred to other precious metal accounts or converted into legal tender at any time.
These accounts serve to store purchasing power. However, this approach does not quite meet the practical requirements for the execution of transactions and the “universal acceptance” mentioned in the chart above.
Stablecoins are blockchain-based units whose price is backed by and firmly pegged to generally recognised assets. If these underlying assets are one or more official currencies, the transfer of a coin economically means the transfer of a currency unit. They do not yet meet the "general acceptance" criterion because only a minority of citizens are technically equipped to receive such coins. Their transfer is possible without the possibility of intervention by central banks or states. Therefore, central banks may feel challenged by stablecoins.
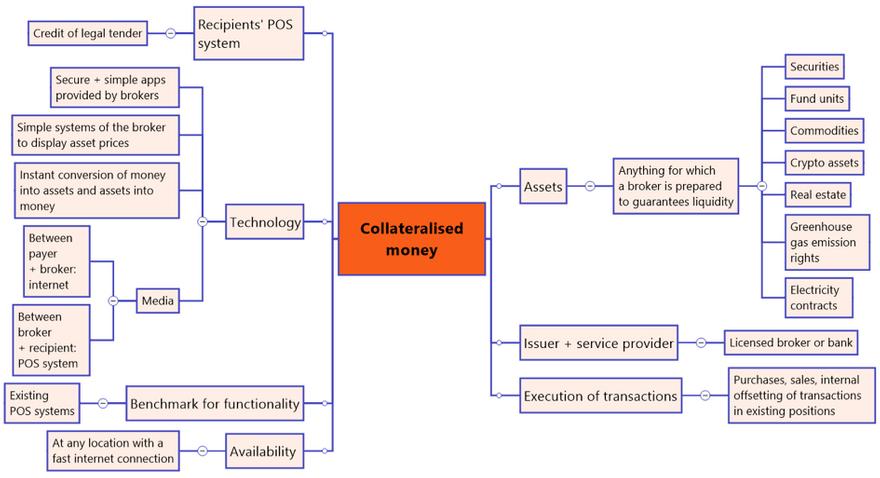
Collateralised money
What we are proposing appears to be a dramatic change. In fact, it is only an acceleration of standard technical processes.
Before we make a major purchase; buying a house for example, we typically sell other assets. These can be securities or a property. Until savings are used for a transaction, we have effectively collateralised purchasing power with assets of our choice. Then we convert these assets into money in order to be able to make a payment of money.
It wouldn't occur to us to do something like that to pay for a yoghurt in a supermarket. For this, the assets in which we have invested for savings seem too bulky. But in fact it is possible to put each asset into a uniform pool and electronically divide and make it available as small as is practically necessary. It makes no technical difference whether a pool consists of stocks, a cryptocurrency, a set of Fabergé eggs or a building plot on Mars. Machines do not start sweating when you ask them to do very small units!
The only precondition is that the assets are permissible and that the owner's broker can provide the exact corresponding amount of legal tender for them in seconds at a fair price after an immediate transaction. The flow of money is triggered via an app on the owner’s electronic device and then goes into the creditor's POS system.
The radical reduction in the time it takes the broker to convert stored purchasing power into legal tender is, from an economic point of view, identical to the collateralisation of money. The remaining time window of perhaps four seconds for the completion of the process does not change this.
An efficient broker can offset transactions within proprietary portfolios or buy and sell in the market at minimal transaction cost. The broker can do this with any asset which is liquid enough to ensure real time settlement.
The broker’s client can decide according to personal preferences which goals (s)he follows with investments (= storage of purchasing power), e.g. avoiding volatility, the inverse correlation with inflation risks or ethical principles. The client can personally steer the portfolio or follow an algorithmically controlled investment procedure.
Here, new asset classes that have been traded at stable prices in the past, but which were previously out of reach for retail clients, may also come into play via qualified brokers: electricity contracts (a cornerstone of our civilisation) and CO2 emission certificates (sovereign risk).
Prudently used autonomy is protection. Mistakes are the results of personal choices.
Chart 2: Collateralised money
Outlook
Money backed by collateral disappeared when it reached practical boundaries.
Programmers are now transcending those practical boundaries. It is likely that in the future, much faster distributed ledger technologies will replace the now reliably functioning POS systems. This does not change the fact that collateralised money is set to return before that system change.
We are on the threshold of the introduction of collateralised money. There are no daunting impediments facing the software that is needed for their implementation. Legislators do not need to take action.
This new money will again be inextricably linked to the real economy, more closely than gold ever was. It will allow citizens to mitigate their economic risk. There will not be any compulsion to use it, but the possibilities are plausible and reassuring.